In a rare reversal for the Indian Space Research Organisation( ISRO), the launch of its 63rd charge involving the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle( PSLV) failed during the third stage of flight. The-rocket,-carrying-the-Earth Observation-Satellite-EOS- 9,-lifted-off-from-the-Satish-Dhawan-Space-Centre-in-Sriharikota-at-559-am-on-May-18,-2025. Though the first two stages performed successfully, the charge encountered an anomaly during the third stage, causing a loss in chamber pressure and eventually leading to charge failure.
Table of Contents
What happed During the Launch?
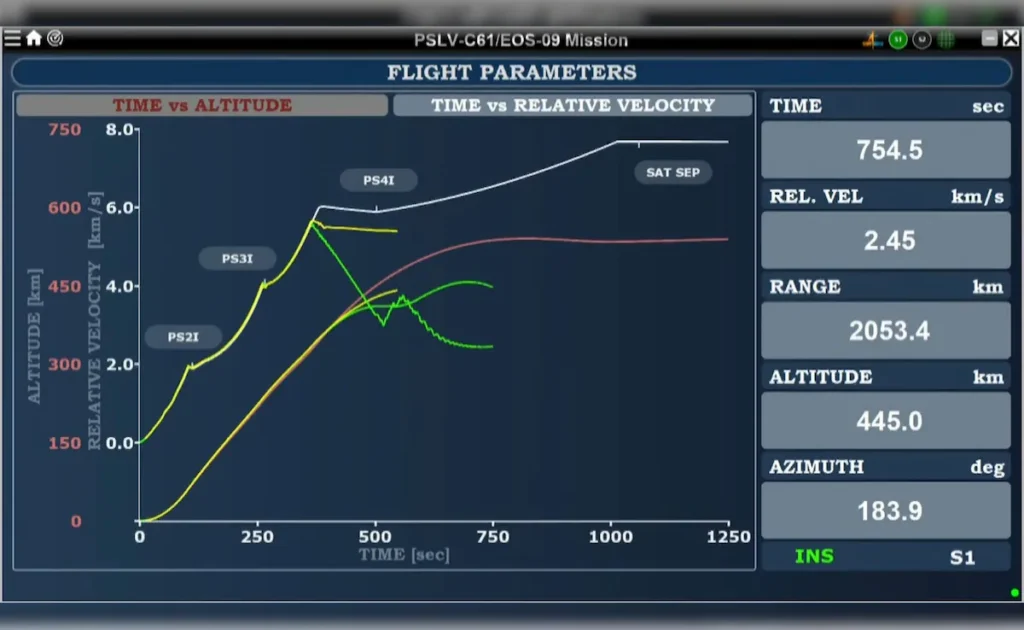
The PSLV- C61 was anticipated to carry EOS- 9 into a sun-coetaneous route 500 kilometers above Earth. This charge marked ISRO’s 101st launch from Sriharikota and was significant for India’s space- grounded surveillance capabilities.
still, shortly after the third stage ignition, ISRO’s ground platoon detected a drop in chamber pressure. According to ISRO Chairman V. Narayanan, the original stages performed negligibly” The third stage motor started rightly, but during its burn phase, an unanticipated observation was noted, leading to charge incompletion.”
Timeline of the PSLV-C61 Mission Attempt
| Stage | Event | Status | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Lift-off and first stage ignition | Success | PSLV lifted off at 5:59 am, powered by solid fuel. |
| Stage 2 | Second stage separation and ignition | Success | Liquid-fueled engine performed as expected. |
| Stage 3 | Third stage ignition and burn phase | Failed | Fall in chamber pressure observed; mission halted. |
| Stage 4 | (Planned) Final burn and satellite deployment | Not Reached | Due to failure in Stage 3, deployment did not proceed. |
EOS- 9 is an Earth Observation Satellite equipped with Synthetic orifice Radar( SAR), giving it the capability to cover Earth in all rainfall conditions, both day and night. It was designed to bolster India’s capabilities in several strategic and mercenary areas
Border surveillance
Agrarian monitoring
Civic planning
Disaster operation
Forestry observation
Had it reached its intended route, EOS- 9 would have significantly enhanced remote seeing operations and strategic intelligence for public security.
What Caused the Failure?
The primary issue was a drop in chamber pressure in the third stage’s solid- energy machine. This stage is responsible for propelling the cargo into advanced mound after the rocket exits Earth’s atmosphere. A chamber pressure drop generally signifies a malfunction in combustion or structural failure within the motor covering.
As per ISRO’s standard operating procedures, both an internal Failure Analysis Committee and an external review board from the Indian government will probe the exact cause. A detailed report is anticipated within a many weeks.

Assignments from the reversal
This failure, while disappointing, is a memorial of the complexity of space operations. The PSLV is known as ISRO’s most dependable launch vehicle, credited with placing the Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan operations into route. This anomaly is rare but not unknown.
Chairman V. Narayanan reaffirmed ISRO’s commitment to translucency and enhancement” We’re reviewing all telemetry data. The cause of the pressure anomaly will be determined, and corrective measures enforced instantly.”
What is Next for ISRO?
The loss of EOS- 9 is a reversal, particularly due to its high- tech cargo and surveillance eventuality. still, India’s constellation of Earth observation satellites, including four radar satellites and eight Cartosats, continues to operate effectively.
The development of a relief for EOS- 9 is anticipated to take 2- 3 times, given the complication of SAR technology. Meanwhile, ISRO plans to do with other operations in its timetable, including Gaganyaan( mortal spaceflight) and Aditya- L1( solar overlook).
Focus on Sustainable Space operations
Interestingly, EOS- 9 was also designed with space sustainability in mind. The satellite had a plannedde-orbiting procedurepost-mission to insure minimum donation to space debris. This visionary planning underscores ISRO’s growing focus on responsible space disquisition.

Conclusion
The failure of the EOS- 9 charge is a moment of reflection but also an occasion for growth. ISRO’s history of adaptability and invention suggests that assignments learned from this reversal will only strengthen unborn operations. The commitment to sustainable practices and transparent disquisition further cements ISRO’s character in the global space community.

1 thought on “ISRO’s EOS-9 Satellite Launch Fails What Went Wrong and What Lies Ahead”