Nasa-Isro
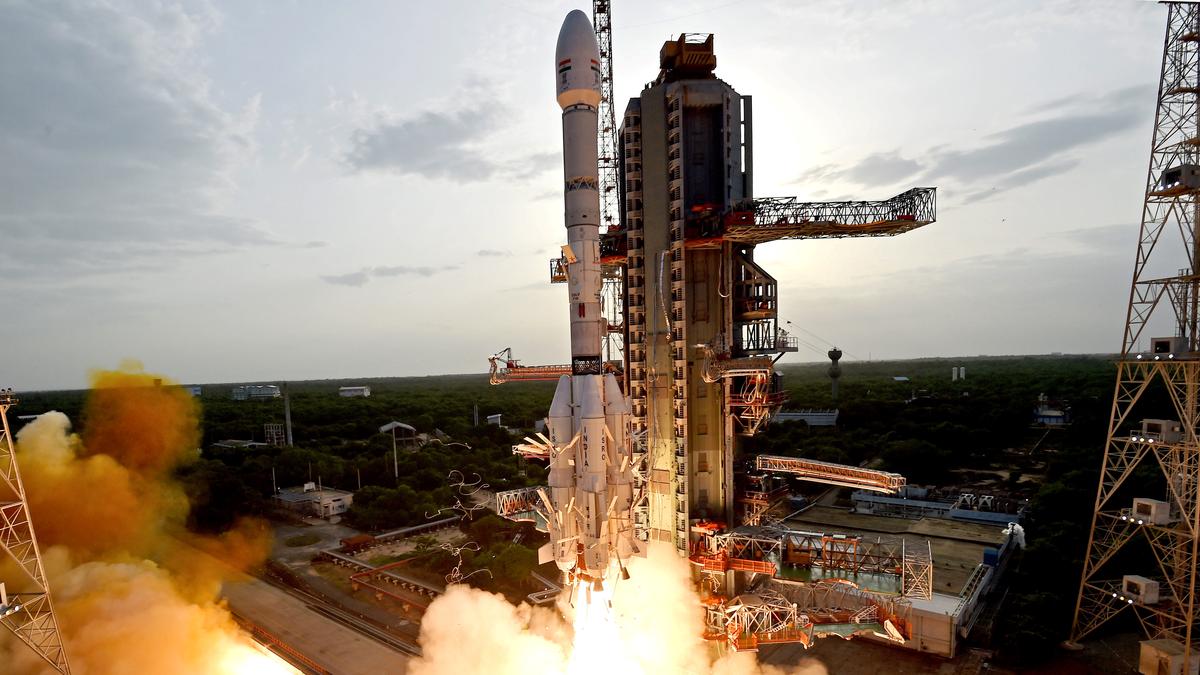
You know, every once in a while, there’s a moment in history that makes you pause and go, “Wow, we’re really doing this.” That’s exactly what happened on July 30, 2025, when India and the United States teamed up to launch something extraordinary — the NISAR satellite. If you haven’t heard about it yet, let me walk you through why this is such a big deal (and why people around the world are geeking out over it!).
Table of Contents
🚀 What is the NISAR Satellite All About?
So, let’s start simple: NISAR stands for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar. It’s not just a cool acronym — it’s a symbol of global collaboration and cutting-edge science NASA-ISRO.
This satellite isn’t just floating around in space for show. It’s built to keep an eye on Earth like never before. Think of it as a space-based detective, capturing tiny movements on land, water, ice, and even vegetation NASA-ISRO.
Quick facts:
- 🌐 Developed by: NASA (USA) + ISRO (India)
- 📍 Launched from: Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh
- 🚀 Vehicle: GSLV-F16 rocket
- 🛰️ Weight: 2,392 kg
- 🕐 Mission Life: 5 years
- 🛸 Orbit: Sun-synchronous polar orbit, 747 km above Earth
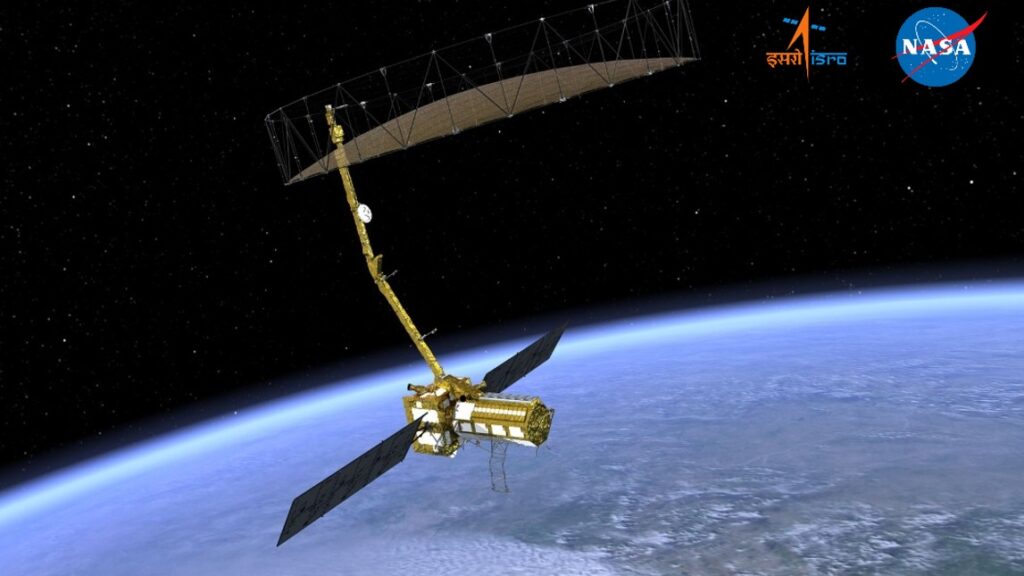
This is the first satellite ever to use dual-frequency radar technology — NASA’s L-band and ISRO’s S-band — in one mission. That’s a pretty huge deal in the space world NASA-ISRO.

🔍 Why NISAR is Such a Game-Changer
Okay, so you might be thinking — it’s just another satellite, right? Well, not really. Here’s why NISAR is a rockstar in the world of Earth observation NASA-ISRO:
1. Disaster Detection & Relief
Ever wished we could predict earthquakes or react faster to floods? NISAR can do that.
- It tracks tectonic shifts, landslides, and ground deformation
- Helps authorities respond quicker to disasters
2. Climate Change Monitoring
With rising global temperatures, ice is melting like never before. NISAR will:
- Monitor ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland
- Track glaciers and sea-level rise
3. Agriculture & Water Resources
Farmers, this one’s for you. The satellite can:
- Map crop patterns
- Detect soil moisture
- Help improve crop yield predictions
4. All-Weather, Day-Night Coverage
NISAR doesn’t take breaks — it works 24/7, in any weather, scanning the Earth every 12 days with super high precision NASA-ISRO.
🔧 How the NASA-ISRO Team Made It Happen
What’s so heartwarming is the collaborative spirit of this mission. Both countries played to their strengths:
| Contribution | NASA | ISRO |
|---|---|---|
| Radar System | L-band SAR | S-band SAR |
| Spacecraft Elements | Reflector antenna, 9m boom | Satellite bus, solar array |
| Launch Services | — | GSLV-F16 rocket |
| Mission Operations | Orbit plan | Satellite control |
The hardware took over 8 years to design, build, and test. This mission wasn’t rushed — it was carefully crafted with precision, love, and a whole lot of expertise NASA-ISRO.

🚦 Mission Timeline at a Glance
Let me break down the mission phases for you:
🚀 Launch Phase
- ✅ Completed on July 30, 2025
- GSLV-F16 nailed the launch, placing NISAR in its orbit like a pro.
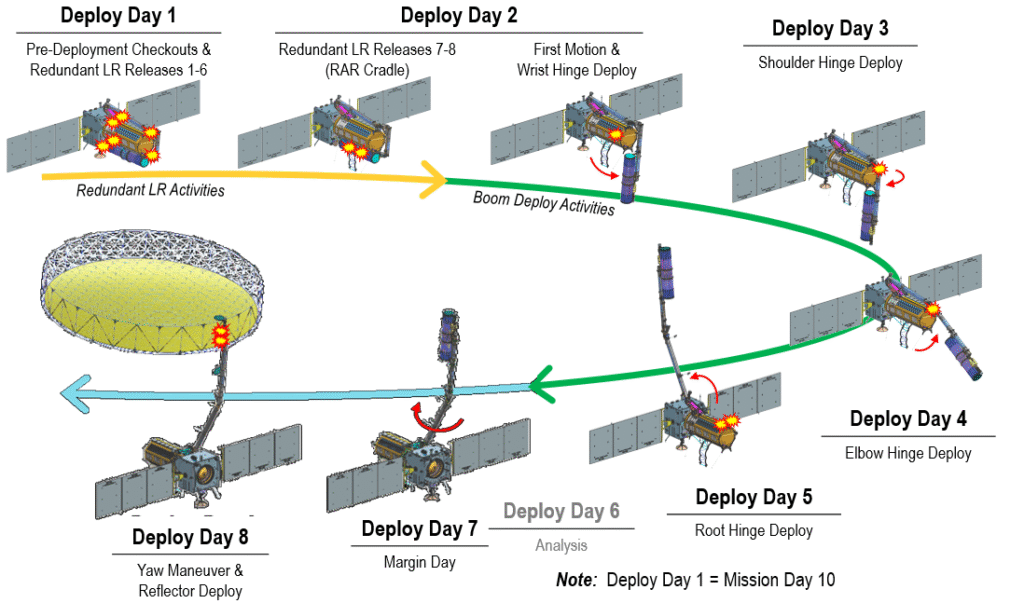
🛰️ Deployment Phase
- Starting around Day 10 after launch
- That iconic 12-meter antenna will unfold like a giant mechanical flower
🔧 Commissioning Phase (First 90 Days)
- System checks
- Calibrations
- Preparing for full science operations
🔬 Science Operations Phase
- Begins after 3 months
- Full-fledged Earth scanning and data collection starts
❓ FAQs About the NISAR Satellite
Q1. What exactly does NISAR do?
NISAR captures radar images of Earth to track changes in land, ice, water, and vegetation. It helps with disaster response, climate change tracking, agriculture monitoring, and more NASA-ISRO.
Q2. How often will NISAR collect data?
Every 12 days, like clockwork. And it works around the clock, rain or shine, day or night NASA-ISRO.
Q3. Is this the first time India and NASA worked together?
It’s their first satellite collaboration, but they’ve partnered before on research and space tech. NISAR is their most ambitious project yet NASA-ISRO.
Q4. Will NISAR data be available to the public?
Yes! NISAR follows a free and open data policy, so scientists and researchers worldwide can access the data.
Q5. Why is the dual-frequency radar so important?
Using both L-band and S-band radars allows NISAR to detect even the tiniest changes on Earth’s surface — like slow-moving landslides or underground water shifts NASA-ISRO.
✅ Final Thoughts: A Proud Moment for Earth… and for Us
Isn’t it just mind-blowing that a piece of tech orbiting hundreds of kilometers above us is quietly watching over our planet — helping us prepare, protect, and plan for a better future?
The NISAR satellite launch is more than just a space event — it’s a reminder of what humanity can achieve when we come together. India and the US, two powerhouses of science and technology, shook hands across borders to do something that could benefit everyone on Earth NASA-ISRO.
So here’s to science, to collaboration, and to caring about our planet. 🌍
We’re not just looking up at the stars anymore. We’re looking down — to understand, protect, and cherish the only home we’ve got NASA-ISRO.
